Limit for imposed working hours
If the conditions for overtime work are met, the employer may impose working hours of up to 10 hours over 7 days, 25 hours over 4 consecutive weeks or 200 hours over 52 weeks (1 year). In addition, total working hours may not exceed 13 hours in a 24-hour period or 48 hours in a 7-day period. However, this limit of 48 hours can be averaged over a period of 8 weeks. This means that it is possible to work more than 48 hours in one week in return for a correspondingly shorter working week in another week.
Companies with a collective agreement can enter into a written agreement on extended overtime work, but it can only be imposed on employees who are willing to do so, and the law sets limits on how much overtime work can be extended. In addition, the Labor Inspectorate can approve applications for extended overtime work in special cases, but here too there are time limits in the law.
Exemption from overtime
If an employee cannot work overtime for social, health or other welfare reasons, he/she may be entitled to be exempted from such work. If the work can be postponed or done by others without harm to the company, this also applies if the employee requests it for personal reasons.
Overtime pay
In the event of overtime work, the employee is entitled to a supplement of at least 40 percent of the agreed hourly wage. It can also be agreed that the employee will take time off for the hours they have worked overtime, hour by hour, but the overtime supplement must still be paid. However, it is common to stipulate better rights in collective agreements than the minimum rights provided by law. Examples of this are that the overtime supplement can be higher than 40 percent, a higher percentage for inconvenient hours (weekends, evenings and public holidays) and/or overtime paid according to the company's agreed working hours.
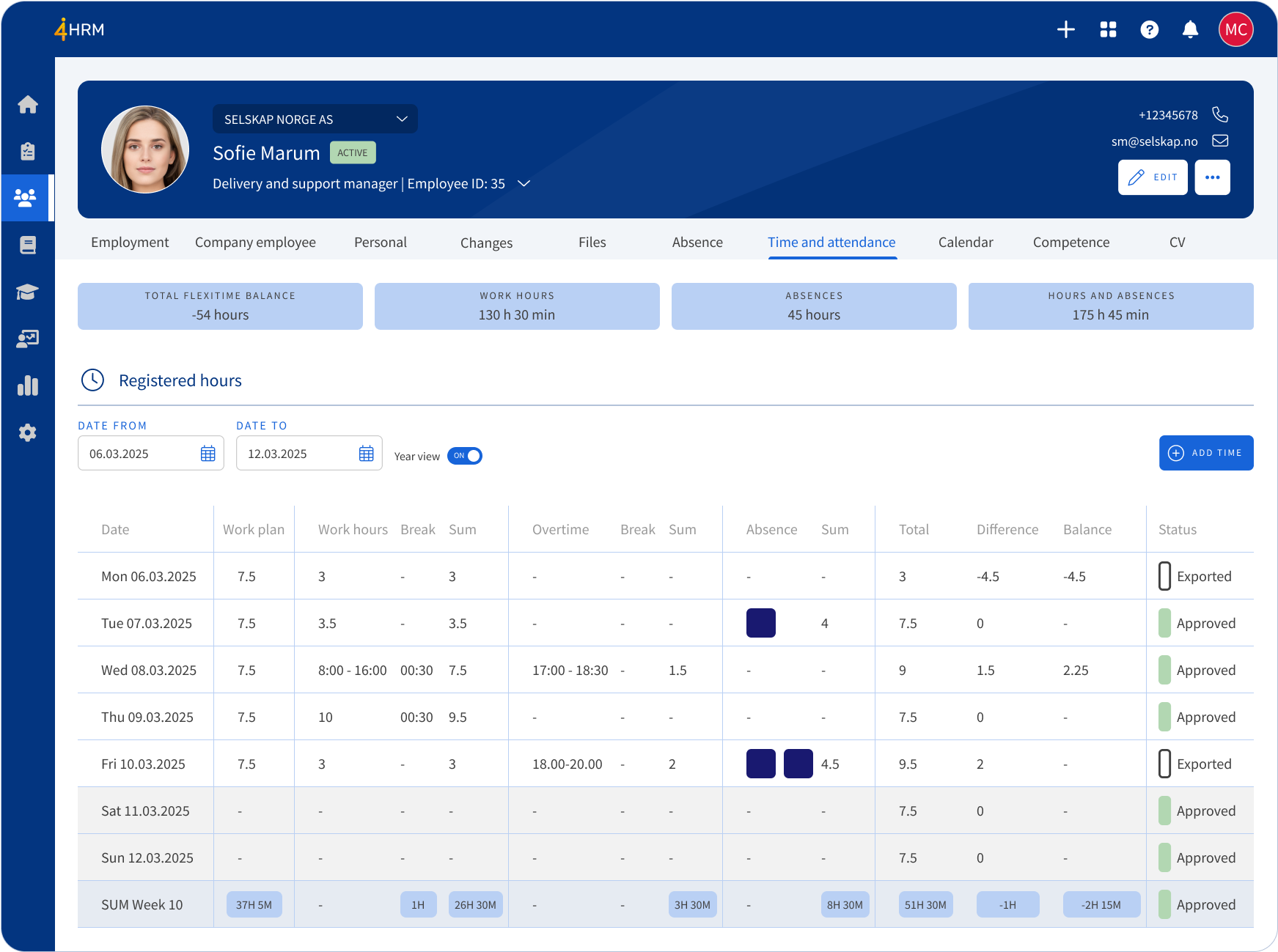
Overtime as time registration
Timesheets are used to register employees' working hours, as well as overtime and flexitime. Updated timesheets provide you as a manager with a basis for payroll and further invoicing.